The Wessex Institute is very active in research covering a number of specialised fields including environmental and electromagnetics, ecology, fluid mechanics, corrosion, damage and fracture, damage tolerance and many others.
The following case studies give an idea of the type of work undertaken by the Institute.
Antibacterial and Antifungal Medical Textiles based on a sono chemical process
A large scale integrated project involving 17 institutions from Europe. As part of the European Commission 7th Framework Programme, the project focused on the application of nanotechnology in medicine. The main objective of this project was to build a pilot line based on the sonochemical process to produce biocidal textiles by impregnating fabrics with antibacterial nanoparticles. The design of the pilot sonochemical reactor was aided by employing computational modelling, which was the main task at WIT. The developed models were used for optimisation of a prototype and for the design of a full scale production line.

Reactor Model
The project included modelling of the mechanical mixing and species transport with reaction and heat transfer in a sonoreactor. The effects of acoustic streaming were included in the model together with the mechanical mixing due to fluid recirculation supported by a pump. The results obtained from these studies provided crucial information for the understanding of the various processes taking place simultaneously inside the reactor. This information was further used for reactor’s operation optimisation.
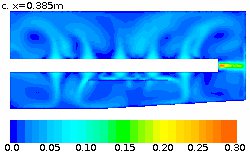
Food Quality and Safety
The main goal of this work, suppored by the European Commission, was the improvement of quality and safety information, transparency and traceability of the chilled/frozen supply food chain by developing cost effective technologies, devices and approaches for continuous monitoring and recording of the relevant data and processing the data for information management throughout the entire supply chain.
The Risk Assessment Work coordinated by WIT included the following specific tasks (i) Risk assessment of microbial and he development of a software tool; Implementation of novel/quantitative modules in the Decision Support System;(ii) Improvement of packaging design, transport and storage (3D models of heat and mass transfer including food structure and mixed culture modelling); (iii) Risk assessment for the concept; (iv) Supply Chain Assessment.
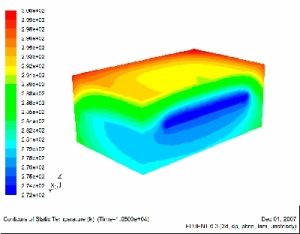
Exposure of the Human Eye to HF Electromagnetic Field
This research involved the developement of efficient methods and codes for the calculation of high frequency electromagnetic fields in lossy media such as human tissue. These codes help to understand certain often overlooked effects, such as the effect of EM fields in the eye at frequencies lower than those present in the visible range. This investigation has identified the focussing effect of such radiation which causes ‘hot spots’, that is temperature gradients exceeding agreed standards.
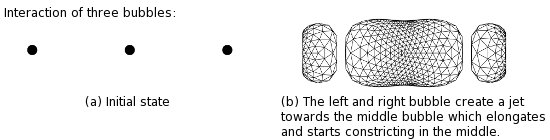
Multiple Bubble Dynamics
Cavitation in liquids is a very important phenomenon which can be considered as a means for energy concentration in the liquid. The collapse of the bubbles can be so rapid that temperatures of thousands of degrees Kelvin and pressures of thousands of atmospheres can be achieved. Such high pressures and temperatures can help the chemical reactions.
Modelling of the bubble dynamics is a moving boundary problem where the interface between the liquid and the gas changes very rapidly. The numerical solution is based on the boundary element method as only the gas-liquid interface needs to be taken into account.
“Life Span Prediction of Hydraulic Turbine Rotors” in collaboration with the University of Sulainmani (Iraq)
The project required 3D simulations of water flow in the Francis turbine runner for different operating conditions combined with stress analysis with the aim to identify possible crack locations in turbine blades.
The pressure distributions on the runner were obtained from this analysis and the results for different boundary conditions were incorporated into a FEM model to calculate the stress distributions. The results indicated that the maximum stresses were situated at the transition between the blades and the crown on the trailing edge, which was verified by the appearance of cracks in these areas.
The models were used for synthetic data generation of the vibration of the turbine runner. The changes in the vibration of the turbine runner were analyzed using the principal component analysis (PCA) combined with artificial neural networks (ANN) and multiple adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems (ANFIS) in order to identify the size and position of the crack.
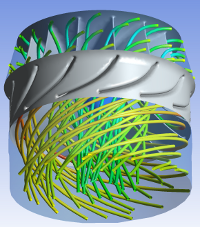
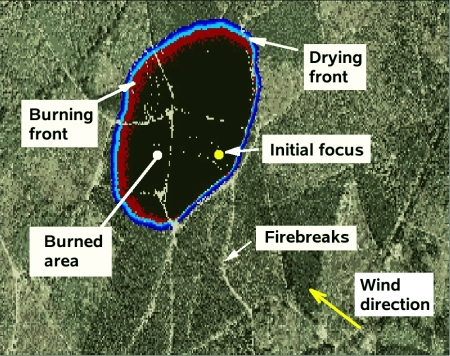
Forest Fires
The project was devoted to the computational modelling of forest fires propagation processes in highly heterogeneous landscapes such as the New Forest National Park where WIT is located. The model is based on a bottom-up approach, i.e. gigascopic characteristics of burning forests such as fire front speed, drying front, and fire-branches in a scale of several kilometres, are derived in terms of microscopic fundamental laws of combustion, heat transfer and fluid dynamics.
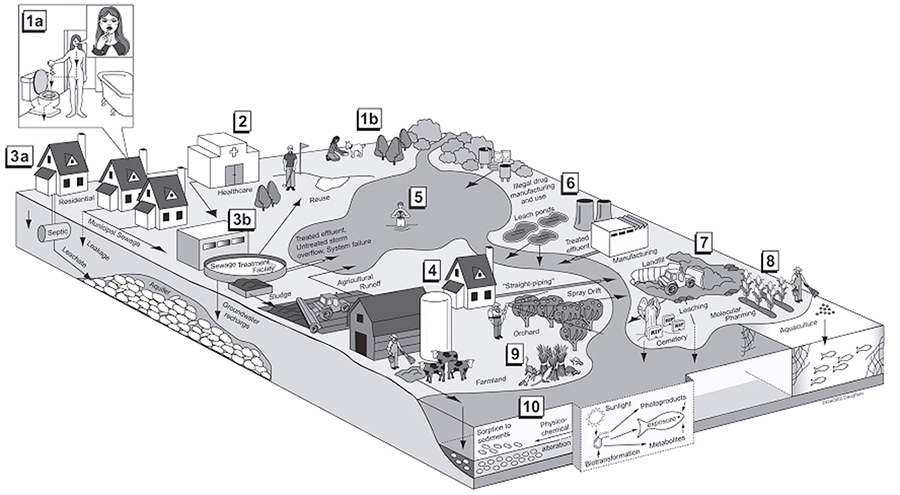
Risk Assessment of Pharmaceutical Products
WIT is the leader of the work on Risk Assessment of pharmaceutical products based on regional, socio-economic and gender factors. Development and employment of novel methods for assessing their origin, fate and effects on human fecundity. It integrated research groups from different disciplines (risk assessors & managers, clinical epidemiologist, endocrinologist, biochemists, as well as experts in biochemical and chemical diagnostics) for a better understanding of the extent of the problem. WIT’s part in the project focused on the risk assessment of Pharmaceutical Products in food and in the environment.
“Sustainable management of the international waters – Prespa Lake”, sponsored by NATO
The Lakes Prespa and Ohrid form a unique hydrological system where the water from the Prespa Lake, which is at 850 m above sea level, drains through the carbonate rocks of the Galichica Mountain into Ohrid Lake, which is at 695 m above sea level. The research study concentrated on experiments to obtain more accurate information on the hydraulic connection between the lakes and on the numerical modelling for a better understanding of the hydrology of the catchment area.

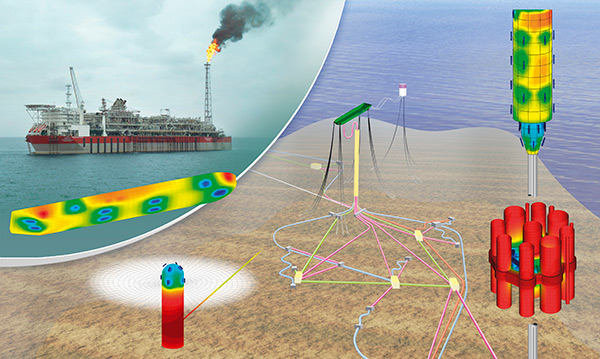
Cathodic Protection
This research, supported by many industry organisations, concentrates on the simulation of cathodic protection to develop optimum corrosion control systems to protect structures and predict their performance over their life-cycle. This work leads the world in simulating galvanic corrosion, optimising CP system design, reducing interference, and in electric and magnetic field protection. There are many important applications of this work in the offshore, oil & gas Industry and naval fields as well as underground infrastructure systems such as pipelines.
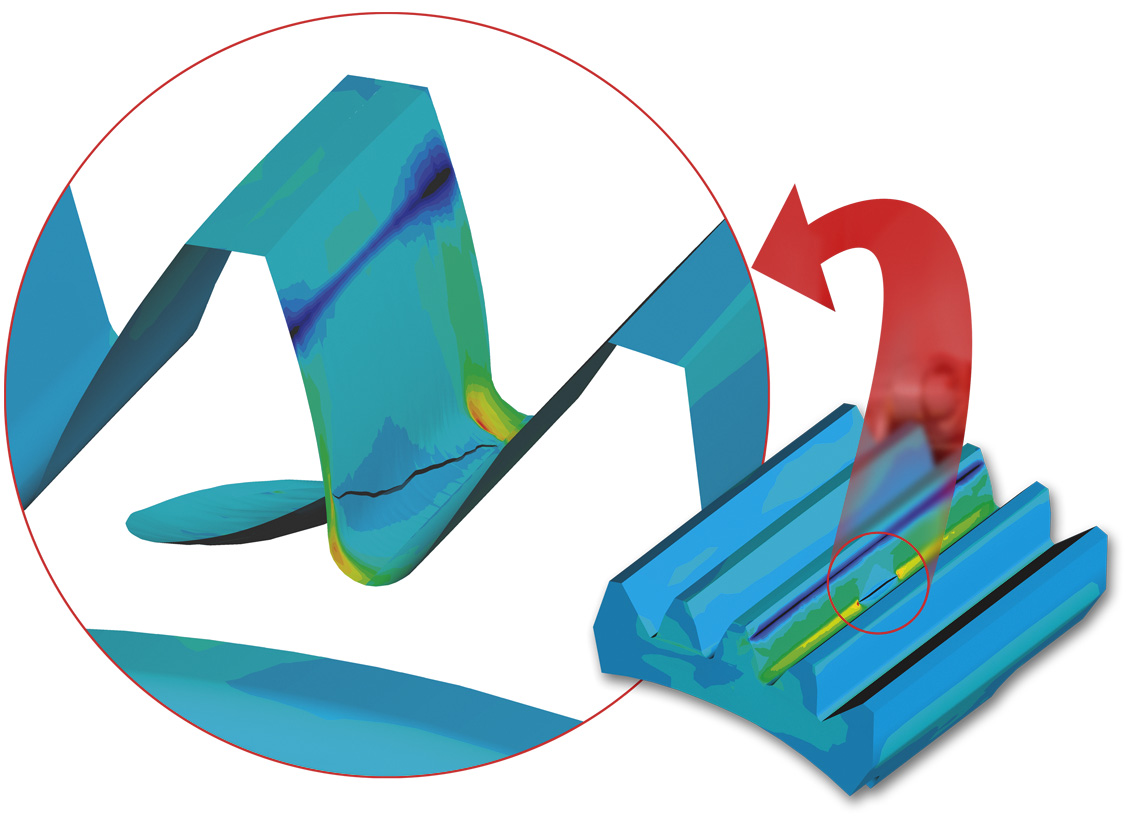
Fracture Mechanics and Crack Propagation
This work is of fundamental importance for product durability prediction. It is based on original methodologies developed at WIT. The resulting software products provide a comprehensive tool for the assessment of the residual strength of damaged structures and the risk of failure. It can be used as part of the design process to predict the impact on components and structure of defects and damage caused by service loads, manufacturing and production process as well as material defects.
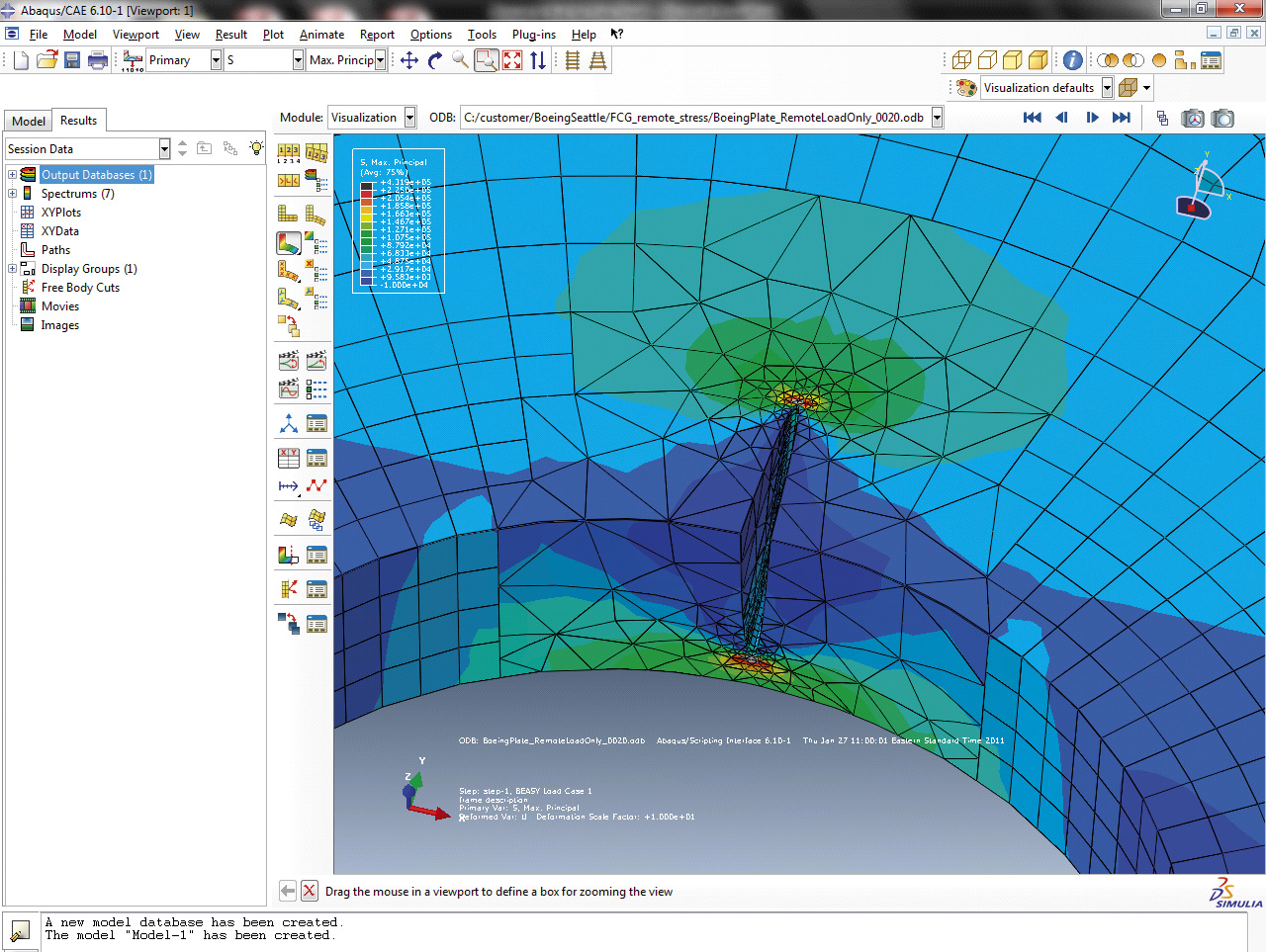
Aircraft Corrosion
This research aimed to develop numerical models capable of simulating corrosion in aircraft structures and was a key part of an EU project. A number of different types of models covering typical corrosion found in aircraft were developed and upscaled for application to structural elements of aircraft. The influence of surface treatment on modelling results was included with regard to inhibitor release from protection systems, role of clad layer and oxide degrading effects. The project provided models that are an essential part of future predictive maintenance concepts to avoid unanticipated and unscheduled maintenance with high costs. Data from monitoring systems and non-destructive inspection can be used as model input. The output from the models can be utilised for the repair decision process to calculate the structural impact of corrosion.

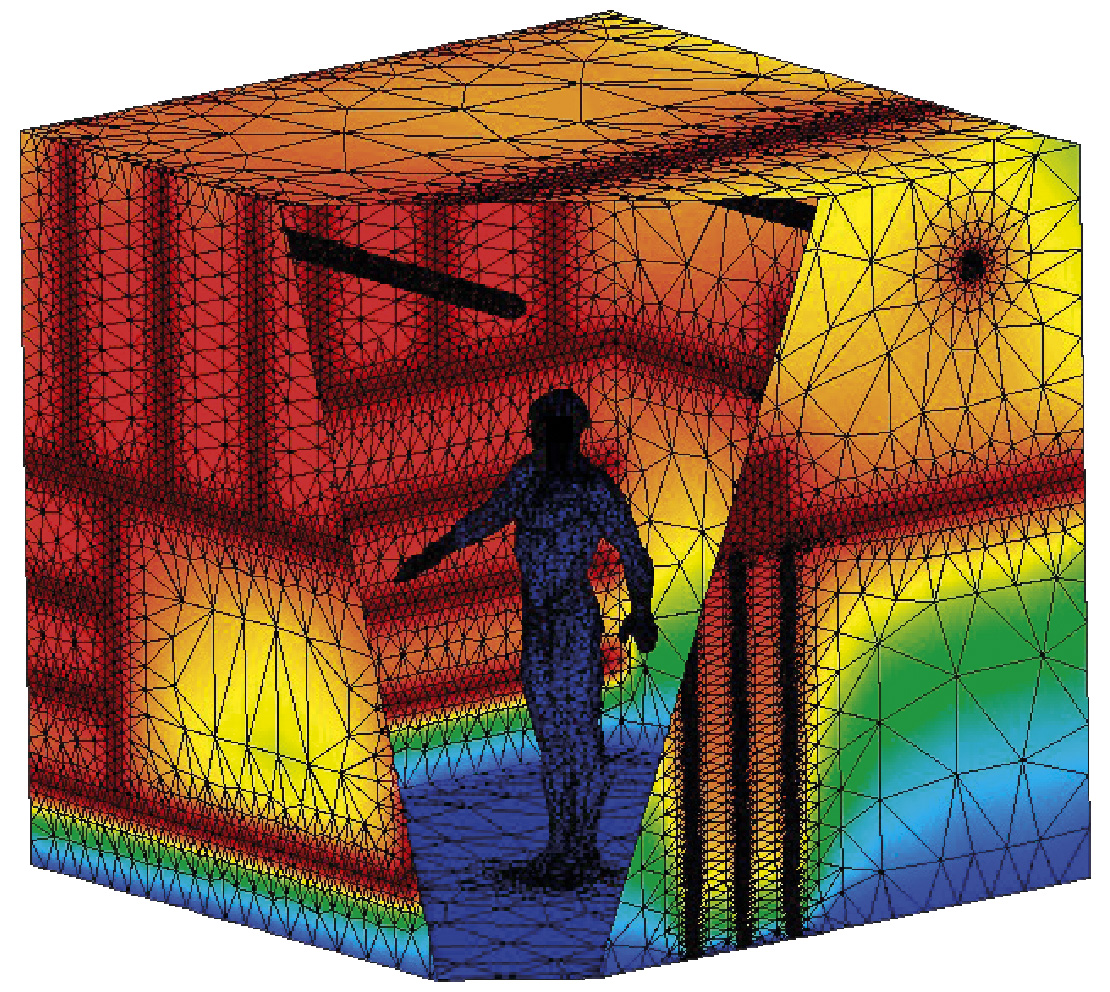
Human Body exposure to ELF Electromagnetic Fields
The project involved the development of different computational models and algorithms for the assessment of human exposure to Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) Electromagnetic fields. Accurate and efficient computational simulation allowed us to detect common situations in which the induced currents inside the body are well above agreed standards.
“Development of direct approaches to tectonic stresses modelling”
The main aim of this project is the development of analytical and numerical tools for the identification of stress fields in the earth’s crust. This project developed alternative theoretical foundations and algorithms to identify tectonic stresses, which involved formulation of mechanically consistent models based on the analysis of observations of stress orientations. Resulting data contributed to the development of new approaches for the prediction of natural and man-induced hazards such as earthquakes, landslides, and tsunami initiation (including developments of early warning systems).
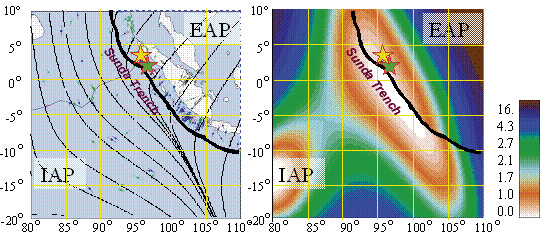
Pattern of stress trajectories (left) and a map of maximum shear stress (right) near Sumatra.
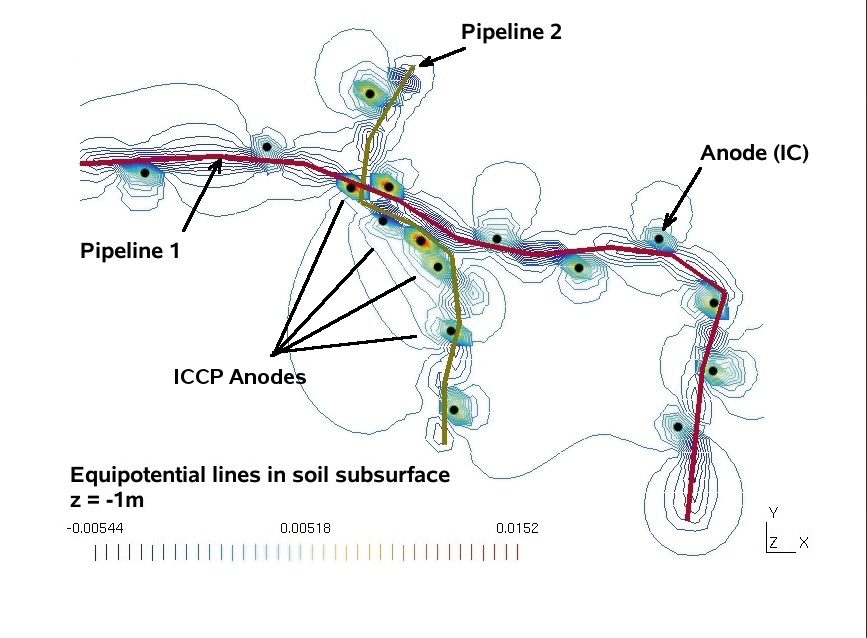
Pipeline Integrity Management
The main objective of the project was to prepare European countries for the hydrogen technology as a source energy using existing infrastructures for natural gas to distribute Hydrogen. The focus of the work was in two areas. Computational modelling of the Cathodic protection system for long transmission pipelines (-600km) connected to a Remote Monitoring System which aims to evaluate the level of protection of the pipeline against corrosion in real time.
The model is capable of forward modelling for analysing what-if scenarios and inverse modelling to detect the size and location of defects in the pipeline coating using data measured at the anodes and other reference cell locations. Prediction of interference with other metallic structures buried in the ground, as well as with other cathodic protection systems is also possible. The model is based on a non-uniform terrain as well as heterogeneous multi-layered media.


 Wessex Institute
Wessex Institute